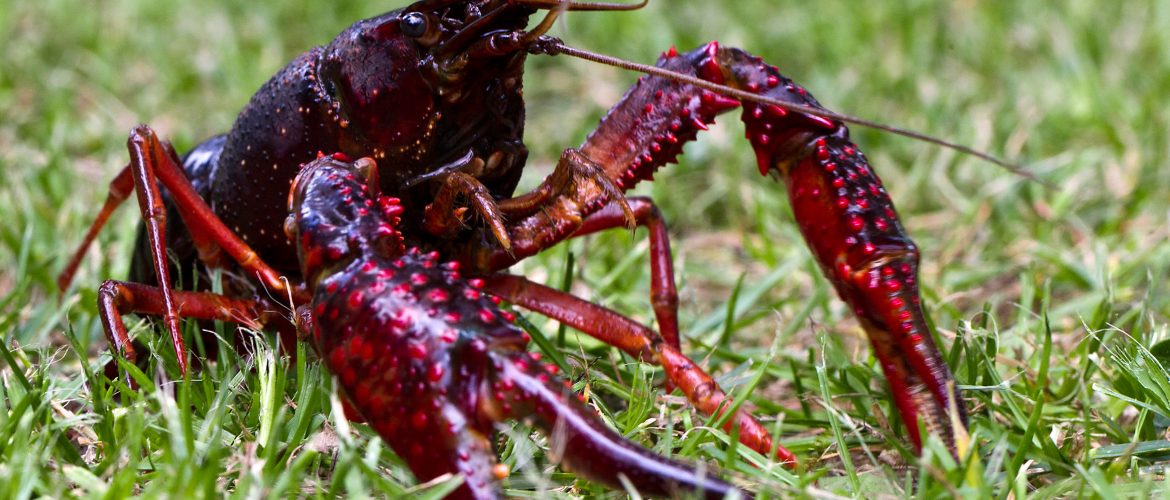
Invasive alien species (IAS) are animals and plants that are introduced accidentally or deliberately into a natural environment where they are not normally found, with serious negative consequences for their new environment. They are a major threat to native plants and animals in Europe and are one of the five major causes of biodiversity loss. They can also cause significant adverse impacts on the economy (their economic impact in the European Union (EU) was estimated at around EUR 12 billion per year) as well as human health, such as severe allergies and burns.
The EU aims to prevent, minimise and mitigate the adverse impacts posed by these species on native biodiversity and ecosystem services. Rules also aim to limit social and economic damage. The EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030 contains the commitment to manage established invasive alien species and decrease the number of Red List species they threaten by 50% by 2030.
The Invasive Alien Species Regulation
The Invasive Alien Species Regulation (Regulation (EU) 1143/2014) includes a set of measures to be taken across the EU in relation to invasive alien species. The core of the Regulation is the list of Invasive Alien Species of Union concern (Union List). The species included on this list are subject to restrictions and measures set out in the Regulation. These include restrictions on keeping, importing, selling, breeding, growing and releasing into the environment.
Member States are required to:
- Take action on pathways of unintentional introduction (i.e. prevention);
- Take measures for the early detection and rapid eradication of these species;
- Manage species that are already widely spread in their territory.
Know more about the effects of invasive alien species on Europe’s biodiversity here.
SETIN took part in the “Atlas Project of Invasive Alien Species in Lazio Region” aimed at reducing the impact of alien fauna species on the regional biodiversity heritage.
Our main responsibilities were:
- Design a geodatabase;
- Define a general strategy for the management of the allochthonous fauna and for the prevention of the entry of new species with the aid of analytical tools considered strategic, including a geodatabase of activities at risk (airports, ports, nurseries, aquaculture, farms, etc.) or the analysis of the risk of entry of new species, based on the study of the methods and vectors of introduction;
- Definition of specific management strategies and action plans, for the taxa for which a more in-depth knowledge is available, containing both the general intervention guidelines and the operational protocols;
- Implementation of concrete actions aimed at preventing entry and reducing the impact of alien fauna species on the biodiversity of Lazio Region.